Digital Transformation is the expression we use to describe the need to adapt businesses to the Digital Age – a time where we face extensive and profound changes in the way technology is managed and consumed.
1. What is Digital Transformation?
Experts signal that the arrival of Industry 4.0 is a direct consequence of the constant digital inclusion, the proliferation of connected objects and the plethora of data available online.
To think about Digital Transformation is to anticipate what is coming, with the steadfast intention of using technology to favors your business.
The Digital Transformation is related to the needs of new habits and interests of the consumer. Since the client journey is not linear, it is important to map the movements with the aim to act in the right way – at the right time.
2. The Digital Transformation culture impact
All the major transformations of the models of production were marked by the search for greater efficiency, cost reduction, and innovation, amongst other points that could converge on growth. And it won’t be any different with Digital Transformation.
As in all other phases, Industry 4.0 will bring social and cultural changes that go beyond technological evolution. There is a long learning curve until companies can take full advantage of the potential of digital technologies and the sectors will evolve gradually according to their specificities.
In the midst of the age of the economy of attention, where the consumer experiences a constant bombardment of information in different channels and devices, companies compete amongst each other for the client’s attention – and also with this broad flow of information. It becomes harder to be relevant. But the challenge is always accompanied by opportunity. And to keep up with all this, technology becomes the greatest ally.
Digital Transformation will be marked by the convergence of digital, physical and biological technologies, impacting several sectors and benefiting the lives of millions of people. Thus, it is not an exaggeration to say that the times in which we live will be known as the age of the revolution of communication and knowledge.
3. Why it matters to your company?
The online vs. offline discussion feels stuck in the past, but the truth is that the integration of these environments remains a challenge for several businesses, from small family businesses to robust multinational corporations.
Some of the reasons for the resistance to change is the myth that the process of Digital Transformation will be very costly and only big companies will have access to changes in infrastructure.
Currently, few companies do not use technology and there is always some investment involved. However, it is not always the case that the costlier solutions are the most appropriate to the corporate needs. Adequate solutions for the clients, as well as partners, tend to be the most efficient and long-lasting.
The good news is that the myths about Digital Transformation are being debunked. According to information from the Confederação Nacional da Indústria (CNI – National Confederation of Industries), Brazilian companies are less shy about using digital technology to increase productivity and reduce costs with equipment maintenance and energy consumption. The increase in work efficiency justifies the investment.
The Fourth Revolution relies on the abundance of data available online and develops with the increasing number of connected devices. The emerging digital technologies, such as the Internet of Things, Big Data, Blockchain and the Artificial Intelligence, for instance, offer a universe of business possibilities and opportunities that are even greater within a short timeframe and investing in the study of at least some of them will be necessary to ensure a slice in the future of the market.
The use of cloud computing also adds to this moment: it is from there that the tools to create new services come from and it is there that the data that they will be based on are stored.
Subscribe to receive our updates
Fill the form to receive our freshest content
4. What is Digital Transformation Good For?
Digital Transformation involves a complete revolution in the way one works and in the way a company makes products available to clients. However, it can be a very painful process for companies that have paved their market trajectories separating business strategies from digital actions.
Currently, it is not enough to improve the business strategy with social networks, digital customer services, and apps to support the performance in the physical world. In comparison to large unicorns that were already born digital, there is a noticeable relationship between success and a business strategy conceived, from the onset, for the digital.
The digital disruption consists of the continuous journey of digitalizing the business, based on insights on the relationship between the consumer and new technology. And by digital one means the elimination of the difference between the physical and the digital. The strategy must be one, integrated and relating to current trends.
The two largest challenges for companies in the process of Digital Transformation are the remodeling of the business for the digital and the digitalization of internal processes.
5. The Digital Transformation Process
Digitization
The unsuspecting readers may believe for an instant that there has been a typo, but the term Digitization came about in 2015 to designate a process of profound transformation of a business to the digital, altering the business model and the flow of value. The Digitization involves a profound structural and strategic change to the business, such as giving up a physical infra-structure to act on an online platform. The term also comprises all the process of integrating value chains of products or services in real time by means of digital platforms and, in summary, can be considered the maximum use of the available technological potential, in an integrated way.
Digitalization
Digital Transformation
6. Driving Digital Transformation
Cloud computing is the distribution of a broad set of online computing services, such as supplying networks, storage and databases, software and servers. Amongst the benefits of cloud computing, are the provision of faster and more flexible access to collaborative innovation tools and the creation of an economy of scale.
Its most widespread business model is the Software as a Service (SaaS), which consists in the distribution of software online by subscription. The giants of the information technology industry have datacenters made of huge installations spread all over the world to host the files of companies safely, to avoid the loss of data and interruption of access.
According to technology experts, data is the new oil. All web browsing leaves traces and, in a world connected like never before, there is a range of opportunities for the collection, interpretation and use of this information on behalf of strategic decision-making.
Big Data refers to this data that grows exponentially and unstructured online and are guided by three factors: data volume, variety and speed. But aside from capturing the data, the determining factor in transforming it into something of value is the judicious analysis of this mass of numbers to transform them into information.
The cross of different discoveries about the user, such as sharing information on different platforms, geolocation, amongst others, allows for the understanding of behavioral factors, motivations and expectations and to adapt them to guide more assertive decisions in your business for a positive impact.
Through structuring the collection of data, Big Data becomes a powerful tool to create insights for a business, anticipate the needs of clients and innovate based on more assertive decisions, generating more efficient business results.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects containing electronic components, such as sensors and software, capable of collecting and exchanging data amongst themselves and with the user. IoT is a technological revolution that aims to connect the objects used in the day to day to the internet. The solutions improve and dynamize the daily experience, improving the efficiency of daily actions.
Each “thing” is identifiable through its computer system but is able to operate within the current structure of the internet. This network of smart objects paves the way to a new horizon of products and services with huge potential to change markets and economies on a global scale – since they are already present in our daily lives.
The applications are as broad and diverse as their disruptive power: implants for cardiac monitors, transponders for farm animals, stock and production control via RFID, automobiles with incorporated sensors, residential automation, security, amongst other solutions.
Not just smart, these objects can also be autonomous, acting according to specific contexts and semantics, accelerating productivity and overcoming infrastructure deficiencies to promote innovation.
Blockchain is a totally decentralized mechanism for registering information, created during the boom of fintechs to validate cryptographed financial transactions, by means of virtual currency such as Bitcoin. The technology offers safety as it relies on distributed systems instead of monolithic to validate digital operations.
This system is based on an architecture of computer networks called Peer-to-Peer (P2P), created to work as the client in addition to as the server, and allows for the sharing of data without the need for a central server. The technology came about initially to facilitate the exchange of music online but reached a new dimension when it served as the basis for the creation of cryptocurrency.
Like with any other monetary system, the virtual transactions also need a record to offer guarantees to the business. It is in this moment that the Blockchain comes in, which can be understood as a set of rules that make the currency work.
In this context, to validate an operation, the Blockchain transmits information to the largest possible number of computers. When a computer accumulates several records about open transactions, it gathers them into a single block and creates a very difficult mathematical notation based on the values of the transaction block.
When a computer solves the problem, the transaction block is considered valid and is distributed to the other computers in the network. The complexity of the mathematical code makes it unlikely that two computers will create a valid transaction block before it is distributed all over the internet.
As the name Blockchain suggests, these blocks are linked, creating a new one, always in reference to a previous, already validated block. In this way, the recent blocks, theoretically, are more vulnerable, but the older blocks become increasingly more secure with the creation of new blocks.
Artificial Intelligence is a computational business that seeks, through technology, to create mechanisms and systems that simulate the human faculties of thinking, solving problems and accumulate learning.
In a practical manner, Artificial Intelligence is based on the capacity of a software to perform human tasks and services at the same time as it learns from situations and refines its workings. In order for this to be possible, the development of a field of technology called Machine Learning is necessary.
This is a method of analyzing data and patterns that automates the construction of more refined models. In this way, all data generated by the technology is automatically used to improve the system, looking to minimize the need for human intervention.
Increasingly more disseminated, today it is possible to find AIs in phones, cars, homes, banks, restaurants, call-centers, Customer Services and several other places. One of the most popular applications are chatbots, programs that simulate human behavior in online conversations via chat. Programming attitudes and phrases, with each interaction the chat refines its system and creates for human-like conversations.
Aside from chats, some AI applications, such as autonomous cars, production lines, transportation logistics and agricultural planning, are already a reality and have relevant impact in the world economy. The trend is for these programs to gain more complexity and have their processing optimized, so that an AI can be inserted in a large variety of services.
7. Agents of Digital Transformation
Digital Transformation is a one-way street – sooner or later, all companies will go down this path. The process of changing to the digital is beneficial for the companies who acquire more adaptable business models and build a DNA of innovation, as well as for the clients, who can enjoy the potential that technology has to offer in an integrated way.
There are three agents of digital transformation that act as driving forces in this process: technology, the non-linear journey and the new business models.
The first propeller of Digital Transformation is, of course, the technology: it is the force capable of making the consumer change his behavior quickly. Some examples of technologies and digital devices go from Bitcoins and Blockchains, to virtual reality NFC payment and wearables, and sensors that work by means of AI.
In a large company, this process of adopting technology is slower than in the world of consumers, as there are inhibiting factors to the transformation, such as a lack of knowledge and the technological-cultural legacy the solution may bring. There is a perception of a large risk involved in changing the business model of a large company, even using innovative technologies.
In this context the sector of Information Technology of companies emerges as a great ally, undertaking a new role. This reassignment makes it so that the actions of the IT professional are no longer operational, but become strategic, acquiring the responsibility of rethinking structural processes.
Some of the benefits include adding to the increase in efficiency and speed of the transformation, eliminating mistakes, reducing operational costs and, consequently, lowering risks. In this way, the IT knowledge is allied with a more efficient and modern management of the business models themselves.
A crucial change becomes the non-linear aspect of the user journey, which makes it more complex and leads to challenges and business opportunities. In the past, the ability to pinpoint the path taken by the client up to the purchase was simpler. Today, there are interactions on several channels before deciding to buy.
In a scenario where the new consumer is over-informed and influenced by a number of points of contact, the scope of the sales funnel is changed, and the functionality of the actions derived from it needs to be reviewed.
In the context of Digital Transformation, merely being mobile-first is already not enough. The rule now is to be digital-first. The market demands planning to perform well in any kind of screen, since the user has a multi-channel behavior. Therefore, to be digital first entails not only prioritizing digital strategies to the detriment of offline ones, but also the reinvention of the business based on the opportunities of the online environment.
To unlock the full potential of the technological innovations of the business, it is essential to create a new corporate culture, more digital and flexible, to anticipate the market trends. In this new stage, the workers should have a collaborative profile, of exchanging ideas with other areas, as well as having empathy for the work of others.
8. The 3 Fronts of Digital Transformation
At MJV, there is the understanding that the process of Digital Transformation can be even more fluid and efficient when it is united with Design Thinking.
Design Thinking, through its techniques of investigation, can supply the necessary understanding about the clients, the Agile Methodologies can decrease the impact of the transition of framework within the teams, eliminating costs and maintaining high productivity and Open Innovation allows for the creation of an ecosystem of innovation that relies on qualified human capital outside the company, producing business ideas in performance spectra that would otherwise not be conceived.
The 3 fronts of Digital Transformation tackled by MJV are:
Digital Mindset
During this stage, there is the redrawing and reframing of processes and routines with a focus on the digital. It includes the implementation of an Agile workspace, the development of digital capabilities within the teams and the development of a digital culture in the sector/company.
Consumer Data-Driven
This is the time to use data to support strategy. It entails the creation of dashboards to ease decision making, the analysis and qualitative approach of the data, whether it be from consumers, clients or sales, as well as the creation of data-driven personas for the assertive development of products and improvement in the processes.

Business Disruption
9. Stages of Adhering to the Digital Strategy
There are stages of adhering to the digital strategy that tell us about how inclined corporations are to the transformation, as well as their acceptance of the digital reality in business and learning curve until adaptive innovation is reached. They can be divided into 4 categories:

Non-Existent or Little Disseminated
Present but not formalized
Operating at a Strategic Level
Adaptive Innovation
10. The impact of Digital Transformation in the sectors
In the digital age, a successful business is that which is constantly rediscovering the value its clients attribute to its product or service. There is the need to establish a synergy with the client, invest in researching interests and change processes, as they become common market practice.
The technology works as an important catalyst for changing behavior in companies, internally as well as externally. However, this metamorphosis does not relate merely to inserting new technologies in the business, but answers also for an entire modification of the organizational structure and culture with the aim of sowing and promoting innovation.
The behavior of the consumer has changed. The dissemination and access to the internet have molded consumer used to getting immediate answers. And the hyper-connectivity of users creates increasingly more unpredictable purchasing journeys.
The hyper-connected client demands products and services more adjusted to his needs since his habits are now different. The new consumers do not stay in hotels like they used to, do not move around the city in the same way, or listen to music or watch movies in the same way.
In this context, the relationship between brands and users takes on a new dimension. The interactions between users and brands become faster and more recurring, drastically increasing the volume of information generated. To be in control of his new phase, companies from different niches need to see technology as a tool that generates business opportunities to ease the connection with the user and ensure more assertive results.
Many think, however, that this is a conversation for the coming years. It will also be. But the Age of Digital Transformation has already begun and several sectors are already aware of the new business opportunities emerging from this change.
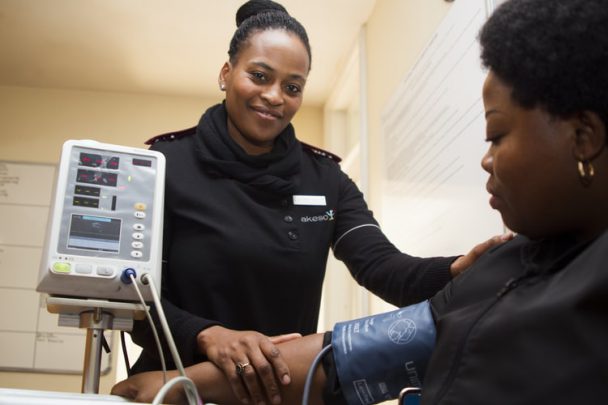
Health
The debate about the technological advances in health has increased considerably amongst are researchers and professionals. When one talks about technological innovation in health, one talks about reducing operational costs and improving productivity to create a positive impact on the patient’s experience.
The future of health goes through the individuality of treatment. Over the last years, hospitals have invested more and more on technologies that contribute to the personalization of diagnosis, as well as to the efficiency of medical procedures, such as telemedicine, neuromedicine, wearables, electronic charts, big data, amongst others.
Currently, health units already rely on virtual consultations for situations where there is not an expert available. Through Telemedicine, for instance, residents in remote areas can receive medical care. With the use of wearable devices, it is possible to monitor one’s own health, amongst other advantages.
The health field is quickly transforming, and the constant evolution of the solutions are driving the development in the sector. As an end result, the digital transformation in the health sector makes it so that people can live longer and with a better quality of life.
Insurance
More connected, well informed and engaged than ever, the insurance sector is aware of the changes happening in consumer behavior. To stay up to date in the competitive Market, companies are using Digital Transformation to redraw their strategies.
The new consumer has high expectations about products offered by insurance companies, demanding a combination of speed, transparency, convenience and security. These characteristics are important to the development of innovative offers, that use technologies such as the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence.
In residential insurances, smartphones linked to sensors installed in the homes allow the user to control alarms and monitor the location. In life insurances, smartwatches and biometric sensors can monitor data such as heart rates, blood pressure, amongst other vital signs of the user, providing constant data that encourage an improvement in healthy habits.
Car insurances are also taken into account. Insurance companies use telemetry to monitor the behavior of users in the vehicles, recording their actions and compiling the videos to identify standards and trace driver profiles.
Quality of Life
Technological applications allow individuals free access to a world of information anywhere. This new reality is directly related to the Digital Transformation, by means of which it was possible to place in devices services which before were associated with physical locations that demanded travel.
Constant visits to doctors offices, for instance, were partially replaced by apps. Diabetics that can test their amounts of insulin, athletes that follow their training and diets, exam results that are sent via e-mail and scheduling exams are some of the activities that before demanded time and effort and are now available on a mobile screen.
The so-called “smart cities” also directly influence the quality of life of citizens. With the help of new technologies, emergency situations can be more quickly resolved, the release of polluting gases are increasingly being diminished, travel times are reduced, as well as all the methods developed to fight violence, robberies and thefts.
More sophisticated forms of surveillance and analysis, relying on the great amounts of data generated by the technologies, optimize practices in health, safety, transportation, amongst others, ensuring Digital Transformation play a key role in increasing the quality of life of citizens.
Residential Automation
The market of Smart Homes is growing and bringing ease to consumers of technology worldwide. Increasing more reliant on Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things, the technological solutions for residential automation are focused on bringing practicality, safety and comfort to the resident.
Amongst the leading trends of the sector, the one that excites the most are the high-resolution smart cameras, with which it will be possible to identify objects, people and movements in order to program specific actions, implement facial recognition once and for all, turn lights on and off automatically, as well as provide security to the environments.
The proper integration of audio, video, lighting and climatization also make possible the Multi-rooms, with multi-zone audio systems that ensure immersion and comfort like never before. All this connected to a single wi-fi, capable of being controlled remotely or, often, by voice recognition.
Transportation
The transportation sector is profoundly affected by Digital Transformation, on the side of personal transportation, as well as of goods.
Planning better routes, correctly estimating the size of trucks for cargo, and tracking fleets by means of GPS, the transportation of goods is constantly optimized to generate even better results. Aside from this, vehicles now have several reports, that enable one to predict problems and defects, detect if the driver is driving correctly and traveling the distances in the planned time.
Personal transportation, on the other hand, also undergoes profound transformations. If private urban transport has become popular due to apps that allow for more affordable prices, for personal vehicles, there are also several technologies emerging that ensure better and safer experiences. In the near future, vehicles will have Artificial Intelligence devices that learn and adapt to the routine of the driver, able to, say, play their favorite radio station, or suggest the best route to work.
Aside from this, electric engines, solar panels and wireless batteries are increasingly more common, gradually lessening the environmental damages and automotive production and maintenance costs.
Teaching
Digital Transformation offers benefits to all involved in the education journey. The main trends in this sector aim to offer autonomy to the student, lessening the burdens on other sectors of the institution, and using Big Data for more personalized and effective educational approaches.
Recently, MJV executed a project with an institution of higher education. With the creation of a self-service gamification app, it was possible to decrease the queues at the administrative offices, the number of complaints and also assist in the student’s journey in several ways, such as creating his schedule, postponing studies, following enrollment, test reminders, emitting documents, amongst other uses. The app also makes study material available and rewards the more engaged students.
The Digital Transformation also allows for the expansion of Distance Learning. In this type of teaching, the teacher and students do not need to physically be in the same space, and classes take place virtually, saving time and money and making the lives of those involved easier. Aside from being practical, Distance Learning also allows knowledge to reach more isolated places, away from the large cities which integrates students once excluded with centers of learning.
On the other hand, the use of Big Data brings direct benefits to a student’s learning, because from it, it is possible to understand which approaches are more assertive and offer better results to the different types of students, identifying problem areas of distraction or lack of motivation, and from them creating more suitable materials.
Clothing and Footwear
The technology has reached the market of clothing and accessories bringing new uses to pieces and capturing important information on well-being and health. The smart shirts, for instance, have sensors capable of detecting heart rate, breathing patterns, location via GPS, amongst several other data that can be shared and analyzed from a mobile phone.
Aside from this, there are the already popular smartwatches, that collect information such as the number of steps, heart rate and quality of sleep, and can also set off alarms according to the settings chosen. This is the case of many diabetics or people undergoing continuous medical treatment, who set their watched to alert them of the correct time to take medication.
Similar functionalities occur in several other products in the market, which already includes electronic backpacks, contain a USB phone charger, pajamas with sensors, to study the quality of sleep of adults and children, and tennis shoes with heaters, to prevent problems in rainy days.
Agrobusiness
From a simple tool to control the harvest to complex tracking systems, the agrobusiness is one of the sectors which most benefits from the Digital Transformation.
The agricultural production, for instance, is more protected and precise when supervised by sensors, whether they be on the ground, connected via the Internet of Things, or aerial, by means of drones. The Internet of Things also reduces costs and increases efficiency by allowing for the insertion of sensors on tractors, fertilizers and harvesters, helping execute tasks such as fertilizing, sowing and harvesting. Indicators such as soil, pH and weather are analyzed in a more precise fashion, ensuring better harvests.
The management of the field also benefits from these technologies, helping rural businessmen in their decision making: GPS that allow for the tracking of fleets, mapping of heat, phytosanitary control, as well as uses for managing teams and sustainable productions lead to increasingly better results on the fields.






