“Why toil away working on the ground when you can take off into the Clouds?“
Ok, we are having a bit of fun here, but the limitless potential of Cloud Computing is something that can’t be denied. From financial services to manufacturing, powerful Cloud solutions deliver a faster time-to-solution and to-market with superior product quality.
You see, Cloud Computing has emerged as the way to democratize information and stands out as an indispensable element for organizations of all segments looking to innovate efficiently.
But what is Cloud Computing, how does it work, and what are all these advantages that everyone seems to be waxing lyrical about? What’s all the fuss about?
Read on for a concise journey of the above, beginning with a couple of eye-catching stats:
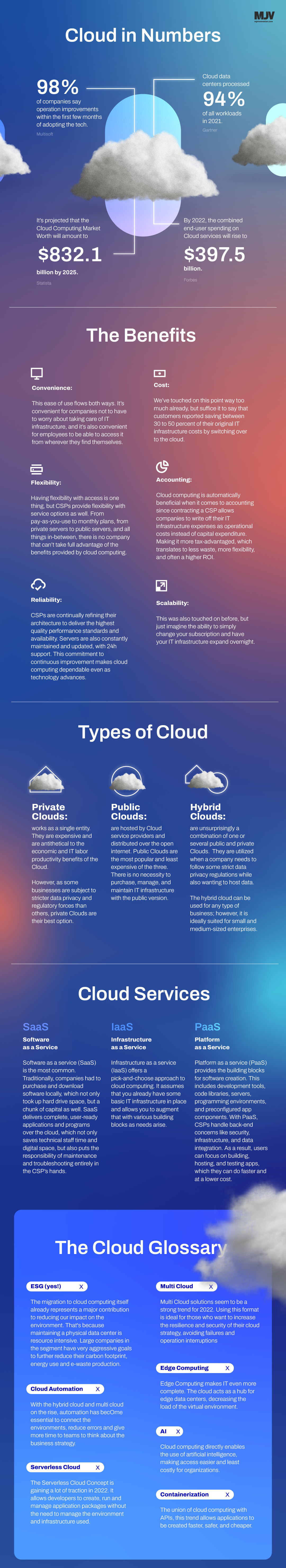
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is an essential technology that allows the remote use of IT resources through the Internet.
It is on-demand access, via the internet, to computing resources—applications, servers, data storage, development tools, networking capabilities, and more—hosted at a remote data center managed by a Cloud service provider.
When using Cloud Computing, it is possible to access software, file storage, and data processing through the internet without connecting to a personal computer or local server. As a result, hardware and software don’t have to be managed, meaning that systems can be accessed anywhere you have access to the internet.
In other words: It lets you ‘plug into’ infrastructure via the internet and use computing resources without installing and maintaining them on-premises.
The outcome of this infrastructure facilitates sharing of documents and simultaneous work.
At the end of the day, all that is genuinely ever required is that all-important quality internet connection.
Cloud technology is used by organizations of all sizes and segments, bringing more flexibility in sharing data and information.
In fact, According to recent reports: “92% of all organizations use some form of the Cloud.”
The most obvious example of Cloud technology is Google Docs, a package of tools that allow creating and editing text documents, spreadsheets, and presentations online without installing any program or file on the computer.
Not surprisingly, many corporations have adopted the Cloud delivery model for their on-premises infrastructure to realize maximum utilization and cost savings rather than sticking to traditional IT infrastructures which can’t provide the same self-service and agility to their end-users.
How Cloud Computing works
At work and in our private lives, we all, almost definitely, use some form of Cloud computing every day. Whether through checking emails or streaming films and shows, we are accessing information that is located on a server somewhere in the world.
But how does Cloud technology work its magic?
The term ‘Cloud computing’ comes from the technology that makes Cloud work. This includes some form of virtualized IT infrastructure—servers, operating system software, networking, and other infrastructure that’s abstracted, using advanced software, that is pooled and divided irrespective of physical hardware boundaries.
A remote server connects users’ devices, such as notebooks, tablets, and cell phones. Basically, all the data and programs users will use will be stored on the server.
Within Cloud computing, there are three different Cloud options:
Private;
Public;
Hybrid.
Ultimately, all three models will grant users access to the files and applications that drive their business anytime, anywhere. The difference lies in how they do it.
Private Clouds
Private Clouds works as a single entity. They are expensive and are antithetical to the economic and IT labor productivity benefits of the Cloud.
However, as some businesses are subject to stricter data privacy and regulatory forces than others, private Clouds are their best option.
Public Clouds
Public Clouds are hosted by Cloud service providers and distributed over the open internet. Public Clouds are the most popular and least expensive of the three.
There is no necessity to purchase, manage, and maintain IT infrastructure with the public version.
Hybrid Clouds
Hybrid Clouds are unsurprisingly a combination of one or several public and private Clouds. They are utilized when a company needs to follow some strict data privacy regulations while also wanting to host data.
The hybrid cloud can be used for any type of business; however, it is ideally suited for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Okay, so we’ve provided some of the basics of what the Cloud is and what makes it work; let’s now cut to the chase and taste some of the benefits.
The advantages of Cloud Computing for your business
Now that we have an understanding of how the technology works, it is time to focus on some of the key advantages of successfully implementing it.
When compared to traditional on-premises IT, and taking into consideration the Cloud services you select and how well it is implemented, the following benefits (which we have categorized into three subheadings) can be delivered:
Cost & accountability;
Convenience & Flexibility;
Agility & Reliability:
1. Cost & accountability
Businesses can save money, become more agile, and operate more efficiently. Companies can reduce their physical IT footprint and eliminate the tediously intensive work of managing data centers.
Substantial savings can also be made by offloading some of the costs and effort of purchasing, installing, configuring, and managing on-premises infrastructure.
Cloud computing is beneficial from an accounting standpoint because it allows IT infrastructure to be classified as operational instead of capital expenditure. This is positive, resulting in better business health because operational expenses are tax-advantaged and pay-as-you-go.
2. Convenience & flexibility
Cloud computing makes storing, recovering, and sharing data fast and easy.
As information streams across locations and devices, employees can work more securely from anywhere, making them more productive, collaborative, and, in theory, satisfied in their jobs.
Cloud solutions also help your workforce at extensive work more efficiently, whether at home, in the office, in a coffee shop, or wherever you might be.
3. Agility & realiability
With Cloud, organizations can use internal applications in minutes instead of waiting weeks or months for IT to respond to a request, purchase and configure supporting hardware, and install the software. Cloud licenses developers and data scientists to authorize themselves to software and support infrastructure.
Cloud service providers are continuously refining their architecture to deliver the highest performance standards. This commitment to improvement makes them dependable in standards of excellence.
All of the above translates to more flexibility, less waste, and better ROI.
Let your company take flight
Ok, so we have shown you the basics of Cloud Computing, but there is so much we haven’t yet touched on here, for example, how best to migrate over to Cloud when your business is ready to make that move?
Well, luckily enough, we have a webinar on that very topic coming up on April 13th. Alternatively, we have a host of material on the subject, including a blog on how best to scale your Cloud Computing.
At the end of the day, the message is simple: Cloud Computing is something companies simply can’t afford to be lagging behind on.
Remember: you don’t have to stay on the ground. To continue the flight analogy from the beginning of this blog and bring everything around full circle, ensure your company takes flight with Cloud Computing.

